Tutorial: Scorecard with binary target¶
In this tutorial, we use the dataset from the FICO Explainable Machine Learning Challenge: https://community.fico.com/s/explainable-machine-learning-challenge. The goal is to develop a scorecard using the logistic regression as an estimator.
[1]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
[2]:
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from optbinning import BinningProcess
from optbinning import Scorecard
from optbinning.scorecard import plot_auc_roc, plot_cap, plot_ks
Download the dataset from the link above and load it.
[3]:
df = pd.read_csv("data/FICO_challenge/heloc_dataset_v1.csv", sep=",")
[4]:
variable_names = list(df.columns[1:])
X = df[variable_names]
Transform the categorical dichotomic target variable into numerical.
[5]:
target = "RiskPerformance"
y = df[target].values
mask = y == "Bad"
y[mask] = 1
y[~mask] = 0
y = y.astype(int)
[6]:
df.head()
[6]:
| RiskPerformance | ExternalRiskEstimate | MSinceOldestTradeOpen | MSinceMostRecentTradeOpen | AverageMInFile | NumSatisfactoryTrades | NumTrades60Ever2DerogPubRec | NumTrades90Ever2DerogPubRec | PercentTradesNeverDelq | MSinceMostRecentDelq | ... | PercentInstallTrades | MSinceMostRecentInqexcl7days | NumInqLast6M | NumInqLast6Mexcl7days | NetFractionRevolvingBurden | NetFractionInstallBurden | NumRevolvingTradesWBalance | NumInstallTradesWBalance | NumBank2NatlTradesWHighUtilization | PercentTradesWBalance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 55 | 144 | 4 | 84 | 20 | 3 | 0 | 83 | 2 | ... | 43 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33 | -8 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 69 |
| 1 | 1 | 61 | 58 | 15 | 41 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 100 | -7 | ... | 67 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | -8 | 0 | -8 | -8 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 67 | 66 | 5 | 24 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 100 | -7 | ... | 44 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 53 | 66 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 86 |
| 3 | 1 | 66 | 169 | 1 | 73 | 28 | 1 | 1 | 93 | 76 | ... | 57 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 72 | 83 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 91 |
| 4 | 1 | 81 | 333 | 27 | 132 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 100 | -7 | ... | 25 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 51 | 89 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 80 |
5 rows × 24 columns
Scorecard development¶
This dataset includes three special values/codes:
-9 No Bureau Record or No Investigation
-8 No Usable/Valid Trades or Inquiries
-7 Condition not Met (e.g. No Inquiries, No Delinquencies)
[7]:
special_codes = [-9, -8, -7]
We specify a selection criteria in terms of the Information Value (IV) predictiveness and minimum quality score to remove low-quality variables. Then, we instantiate a BinningProcess object class with variable names, special codes and selection criteria.
[8]:
selection_criteria = {
"iv": {"min": 0.02, "max": 1},
"quality_score": {"min": 0.01}
}
[9]:
binning_process = BinningProcess(variable_names, special_codes=special_codes,
selection_criteria=selection_criteria)
We select as an estimator a logistic regression to be solved using the non-linear solver L-BFGS-B.
[10]:
estimator = LogisticRegression(solver="lbfgs")
Finally, we instantiate a Scorecard class with the target name, a binning process object, and an estimator. In addition, we want to apply a scaling method to the scorecard points.
[11]:
scorecard = Scorecard(binning_process=binning_process,
estimator=estimator, scaling_method="min_max",
scaling_method_params={"min": 300, "max": 850})
[12]:
scorecard.fit(X, y, show_digits=4)
/home/gui/projects/github/top/optbinning/optbinning/binning/transformations.py:38: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in log
return np.log((1. / event_rate - 1) * n_event / n_nonevent)
[12]:
Scorecard(binning_process=BinningProcess(selection_criteria={'iv': {'max': 1,
'min': 0.02},
'quality_score': {'min': 0.01}},
special_codes=[-9, -8, -7],
variable_names=['ExternalRiskEstimate',
'MSinceOldestTradeOpen',
'MSinceMostRecentTradeOpen',
'AverageMInFile',
'NumSatisfactoryTrades',
'NumTrades60Ever2DerogPubRec',
'NumTrades90Ever2DerogPubRec',
'PercentTradesNe...
'PercentInstallTrades',
'MSinceMostRecentInqexcl7days',
'NumInqLast6M',
'NumInqLast6Mexcl7days',
'NetFractionRevolvingBurden',
'NetFractionInstallBurden',
'NumRevolvingTradesWBalance',
'NumInstallTradesWBalance',
'NumBank2NatlTradesWHighUtilization',
'PercentTradesWBalance']),
estimator=LogisticRegression(), scaling_method='min_max',
scaling_method_params={'max': 850, 'min': 300})
Similar to other objects in OptBinning, we can print overview information about the options settings, problems statistics, and the number of selected variables after the binning process. With these settings, using the selection criteria, 4 variables are removed.
[13]:
scorecard.information(print_level=2)
optbinning (Version 0.19.0)
Copyright (c) 2019-2024 Guillermo Navas-Palencia, Apache License 2.0
Begin options
binning_process yes * U
estimator yes * U
scaling_method min_max * U
scaling_method_params yes * U
intercept_based False * d
reverse_scorecard False * d
rounding False * d
verbose False * d
End options
Statistics
Number of records 10459
Number of variables 23
Target type binary
Number of numerical 23
Number of categorical 0
Number of selected 19
Timing
Total time 3.28 sec
Binning process 2.62 sec ( 79.92%)
Estimator 0.25 sec ( 7.70%)
Build scorecard 0.41 sec ( 12.36%)
rounding 0.00 sec ( 0.00%)
The method table returns the scorecard table. A scorecard table has a wide range of real-world business applications, being an interpretable tool to summarize relationships among variables. The scorecard table can handle binary and continuous targets. Two scorecard styles are available: style="summary" shows the variable name, and their corresponding bins and assigned points; style="detailed" adds information from the corresponding binning table.
[14]:
scorecard.table(style="summary")
[14]:
| Variable | Bin | Points | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ExternalRiskEstimate | (-inf, 59.5000) | 5.359275 |
| 1 | ExternalRiskEstimate | [59.5000, 63.5000) | 11.598078 |
| 2 | ExternalRiskEstimate | [63.5000, 65.5000) | 18.168973 |
| 3 | ExternalRiskEstimate | [65.5000, 67.5000) | 19.821705 |
| 4 | ExternalRiskEstimate | [67.5000, 70.5000) | 25.498720 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 8 | PercentTradesWBalance | [80.5000, 87.5000) | 32.310289 |
| 9 | PercentTradesWBalance | [87.5000, 98.0000) | 32.026880 |
| 10 | PercentTradesWBalance | [98.0000, inf) | 31.928758 |
| 11 | PercentTradesWBalance | Special | 32.738612 |
| 12 | PercentTradesWBalance | Missing | 32.738612 |
164 rows × 3 columns
[15]:
scorecard.table(style="detailed")
[15]:
| Variable | Bin id | Bin | Count | Count (%) | Non-event | Event | Event rate | WoE | IV | JS | Coefficient | Points | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ExternalRiskEstimate | 0 | (-inf, 59.5000) | 1081 | 0.103356 | 166 | 915 | 0.846438 | -1.619109 | 0.217629 | 0.024574 | -0.327969 | 5.359275 |
| 1 | ExternalRiskEstimate | 1 | [59.5000, 63.5000) | 1097 | 0.104886 | 228 | 869 | 0.792160 | -1.250170 | 0.142003 | 0.016678 | -0.327969 | 11.598078 |
| 2 | ExternalRiskEstimate | 2 | [63.5000, 65.5000) | 681 | 0.065111 | 190 | 491 | 0.720999 | -0.861592 | 0.044754 | 0.005427 | -0.327969 | 18.168973 |
| 3 | ExternalRiskEstimate | 3 | [65.5000, 67.5000) | 652 | 0.062339 | 195 | 457 | 0.700920 | -0.763856 | 0.034156 | 0.004169 | -0.327969 | 19.821705 |
| 4 | ExternalRiskEstimate | 4 | [67.5000, 70.5000) | 1038 | 0.099245 | 388 | 650 | 0.626204 | -0.428139 | 0.017755 | 0.002203 | -0.327969 | 25.498720 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 8 | PercentTradesWBalance | 8 | [80.5000, 87.5000) | 797 | 0.076202 | 283 | 514 | 0.644918 | -0.508949 | 0.019114 | 0.002364 | -0.016322 | 32.310289 |
| 9 | PercentTradesWBalance | 9 | [87.5000, 98.0000) | 652 | 0.062339 | 184 | 468 | 0.717791 | -0.845705 | 0.041380 | 0.005024 | -0.016322 | 32.026880 |
| 10 | PercentTradesWBalance | 10 | [98.0000, inf) | 1277 | 0.122096 | 331 | 946 | 0.740799 | -0.962296 | 0.103054 | 0.012407 | -0.016322 | 31.928758 |
| 11 | PercentTradesWBalance | 11 | Special | 606 | 0.057941 | 269 | 337 | 0.556106 | -0.137544 | 0.001091 | 0.000136 | -0.016322 | 32.738612 |
| 12 | PercentTradesWBalance | 12 | Missing | 0 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | -0.016322 | 32.738612 |
164 rows × 13 columns
We can check the correctness of the scaling method as follows
[16]:
sc = scorecard.table(style="summary")
sc.groupby("Variable").agg({'Points' : [np.min, np.max]}).sum()
[16]:
Points amin 300.0
amax 850.0
dtype: float64
Scorecard performance¶
Compute predicted probabilities of the fitted estimator.
[17]:
y_pred = scorecard.predict_proba(X)[:, 1]
/home/gui/projects/github/top/optbinning/optbinning/binning/transformations.py:38: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in log
return np.log((1. / event_rate - 1) * n_event / n_nonevent)
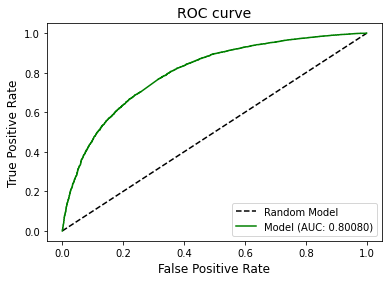
Plot Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (AUC ROC).
[18]:
plot_auc_roc(y, y_pred)
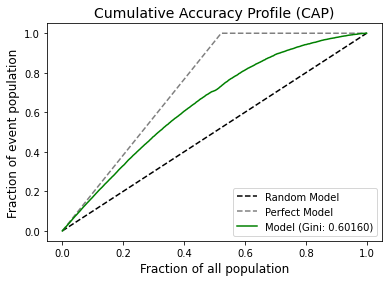
Plot Cumulative Accuracy Profile (CAP).
[19]:
plot_cap(y, y_pred)
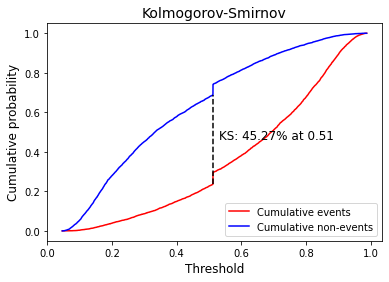
Plot Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS).
[20]:
plot_ks(y, y_pred)
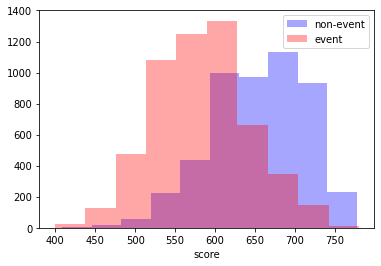
Calculate the score of the dataset and plot distribution of scores for event and non-event records.
[21]:
score = scorecard.score(X)
[22]:
mask = y == 0
plt.hist(score[mask], label="non-event", color="b", alpha=0.35)
plt.hist(score[~mask], label="event", color="r", alpha=0.35)
plt.xlabel("score")
plt.legend()
plt.show()