Tutorial: optimal binning with binary target - LocalSolver¶
To get us started, let’s load the application_train.csv file from the Kaggle’s competition https://www.kaggle.com/c/home-credit-default-risk/data.
[1]:
import pandas as pd
[2]:
df = pd.read_csv("data/kaggle/HomeCreditDefaultRisk/application_train.csv", engine='c')
We choose a variable to discretize and the binary target.
[3]:
variable = "REGION_POPULATION_RELATIVE"
x = df[variable].values
y = df.TARGET.values
Import and instantiate an OptimalBinning object class. We pass the variable name, its data type, and a solver, in this case, we choose the commercial solver LocalSolver. Note that LocalSolver requires a time limit, which is set to 20 seconds (LocalSolver 10.0). Besides, for this example, we require a more granular binning, therefore we allow a large number of prebins with small size.
To use LocalSolver follow the avaiable instructions: https://www.localsolver.com/docs/last/quickstart/solvingyourfirstmodelinpython.html
[4]:
from optbinning import OptimalBinning
[5]:
optb = OptimalBinning(name=variable, dtype="numerical", solver="ls", max_n_prebins=100,
min_prebin_size=0.001, time_limit=20)
We fit the optimal binning object with arrays x and y.
[6]:
optb.fit(x, y)
Push initial solution 100%
Model: expressions = 79028, decisions = 309, constraints = 6161, objectives = 1
Param: time limit = 20 sec, no iteration limit
[objective direction ]: maximize
[ 0 sec, 0 itr]: 0
[ optimality gap ]: 100.00%
[ 1 sec, 0 itr]: 0
[ 2 sec, 1650 itr]: 34776
[ 3 sec, 6276 itr]: 37297
[ 4 sec, 6276 itr]: 37297
[ 5 sec, 8516 itr]: 37297
[ 6 sec, 10771 itr]: 37297
[ 7 sec, 12813 itr]: 37297
[ 8 sec, 15256 itr]: 37305
[ 9 sec, 17634 itr]: 37305
[ 10 sec, 20136 itr]: 37305
[ optimality gap ]: 82.27%
[ 11 sec, 22303 itr]: 37305
[ 12 sec, 24608 itr]: 37729
[ 13 sec, 26865 itr]: 37758
[ 14 sec, 28828 itr]: 37758
[ 15 sec, 33133 itr]: 37758
[ 16 sec, 33133 itr]: 37758
[ 17 sec, 35139 itr]: 37758
[ 18 sec, 37028 itr]: 37758
[ 19 sec, 40000 itr]: 37758
[ 20 sec, 40000 itr]: 37758
[ optimality gap ]: 82.06%
[ 20 sec, 40000 itr]: 37758
[ optimality gap ]: 82.06%
40000 iterations performed in 20 seconds
Feasible solution:
obj = 37758
gap = 82.06%
bounds = 210419
[6]:
OptimalBinning(cat_cutoff=None, class_weight=None, divergence='iv',
dtype='numerical', gamma=0, max_bin_n_event=None,
max_bin_n_nonevent=None, max_bin_size=None, max_n_bins=None,
max_n_prebins=100, max_pvalue=None,
max_pvalue_policy='consecutive', min_bin_n_event=None,
min_bin_n_nonevent=None, min_bin_size=None,
min_event_rate_diff=0, min_n_bins=None, min_prebin_size=0.001,
mip_solver='bop', monotonic_trend='auto',
name='REGION_POPULATION_RELATIVE', outlier_detector=None,
outlier_params=None, prebinning_method='cart', solver='ls',
special_codes=None, split_digits=None, time_limit=20,
user_splits=None, user_splits_fixed=None, ...)
You can check if an optimal or feasible solution has been found via the status attribute:
[7]:
optb.status
[7]:
'FEASIBLE'
[8]:
binning_table = optb.binning_table
binning_table.build()
binning_table.analysis()
---------------------------------------------
OptimalBinning: Binary Binning Table Analysis
---------------------------------------------
General metrics
Gini index 0.08180326
IV (Jeffrey) 0.03776231
JS (Jensen-Shannon) 0.00465074
Hellinger 0.00468508
Triangular 0.01833822
KS 0.06087208
HHI 0.23425608
HHI (normalized) 0.16464300
Cramer's V 0.05102627
Quality score 0.06257516
Monotonic trend peak
Significance tests
Bin A Bin B t-statistic p-value P[A > B] P[B > A]
0 1 1.445262 2.292897e-01 1.013041e-01 8.986959e-01
1 2 158.939080 1.929529e-36 1.179082e-218 1.000000e+00
2 3 131.200666 2.238000e-30 1.000000e+00 1.110223e-16
3 4 0.878638 3.485750e-01 8.240457e-01 1.759543e-01
4 5 14.925402 1.118468e-04 9.999989e-01 1.123668e-06
5 6 3.969732 4.632513e-02 9.768847e-01 2.311530e-02
6 7 40.662233 1.809509e-10 1.000000e+00 3.330669e-16
7 8 29.296187 6.211781e-08 1.000000e+00 4.795286e-11
8 9 10.992632 9.147483e-04 9.997649e-01 2.351244e-04
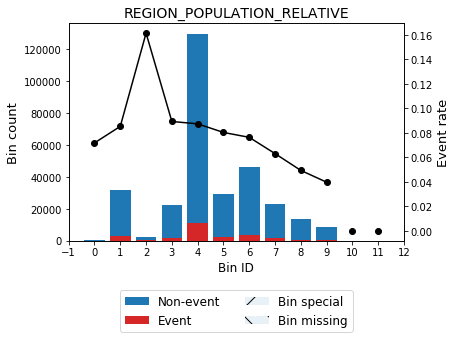
[9]:
binning_table.plot(metric="event_rate")
[10]:
optb.information(print_level=1)
optbinning (Version 0.18.0)
Copyright (c) 2019-2023 Guillermo Navas-Palencia, Apache License 2.0
Name : REGION_POPULATION_RELATIVE
Status : FEASIBLE
Pre-binning statistics
Number of pre-bins 77
Number of refinements 0
Solver statistics
Type ls
Number of iterations 40000
Timing
Total time 21.43 sec
Pre-processing 0.01 sec ( 0.05%)
Pre-binning 0.50 sec ( 2.35%)
Solver 20.91 sec ( 97.59%)
Post-processing 0.00 sec ( 0.00%)
Computing the optimal binning starting with a large number of prebins might be challenging in some situations, therefore solvers such as LocalSolver are suitable to find quality feasible solutions in a reasonable amount of time. However, if LocalSolver is not available we can always try solver options “cp” or “mip”.
Constraint programming solver¶
First, we keep the 5 seconds time limit:
[11]:
optb = OptimalBinning(name=variable, dtype="numerical", solver="cp", max_n_prebins=100,
min_prebin_size=0.001, time_limit=5)
[12]:
optb.fit(x, y)
[12]:
OptimalBinning(cat_cutoff=None, class_weight=None, divergence='iv',
dtype='numerical', gamma=0, max_bin_n_event=None,
max_bin_n_nonevent=None, max_bin_size=None, max_n_bins=None,
max_n_prebins=100, max_pvalue=None,
max_pvalue_policy='consecutive', min_bin_n_event=None,
min_bin_n_nonevent=None, min_bin_size=None,
min_event_rate_diff=0, min_n_bins=None, min_prebin_size=0.001,
mip_solver='bop', monotonic_trend='auto',
name='REGION_POPULATION_RELATIVE', outlier_detector=None,
outlier_params=None, prebinning_method='cart', solver='cp',
special_codes=None, split_digits=None, time_limit=5,
user_splits=None, user_splits_fixed=None, ...)
The status is “UNKNOWN” therefore nor feasible or optimal solutions was found in 5 seconds.
[13]:
optb.status
[13]:
'UNKNOWN'
[14]:
optb.information(print_level=1)
optbinning (Version 0.18.0)
Copyright (c) 2019-2023 Guillermo Navas-Palencia, Apache License 2.0
Name : REGION_POPULATION_RELATIVE
Status : UNKNOWN
Pre-binning statistics
Number of pre-bins 77
Number of refinements 0
We increase the time limit to 30 seconds.
[15]:
optb = OptimalBinning(name=variable, dtype="numerical", solver="cp", max_n_prebins=100,
min_prebin_size=0.001, time_limit=30)
[16]:
optb.fit(x, y)
[16]:
OptimalBinning(cat_cutoff=None, class_weight=None, divergence='iv',
dtype='numerical', gamma=0, max_bin_n_event=None,
max_bin_n_nonevent=None, max_bin_size=None, max_n_bins=None,
max_n_prebins=100, max_pvalue=None,
max_pvalue_policy='consecutive', min_bin_n_event=None,
min_bin_n_nonevent=None, min_bin_size=None,
min_event_rate_diff=0, min_n_bins=None, min_prebin_size=0.001,
mip_solver='bop', monotonic_trend='auto',
name='REGION_POPULATION_RELATIVE', outlier_detector=None,
outlier_params=None, prebinning_method='cart', solver='cp',
special_codes=None, split_digits=None, time_limit=30,
user_splits=None, user_splits_fixed=None, ...)
In 30 seconds we found a feasible solution
[17]:
optb.status
[17]:
'FEASIBLE'
[18]:
optb.information(print_level=1)
optbinning (Version 0.18.0)
Copyright (c) 2019-2023 Guillermo Navas-Palencia, Apache License 2.0
Name : REGION_POPULATION_RELATIVE
Status : FEASIBLE
Pre-binning statistics
Number of pre-bins 77
Number of refinements 0
Solver statistics
Type cp
Number of booleans 3155
Number of branches 28213
Number of conflicts 6885
Objective value 37367
Best objective bound 74233
Timing
Total time 49.50 sec
Pre-processing 0.00 sec ( 0.01%)
Pre-binning 0.45 sec ( 0.90%)
Solver 49.05 sec ( 99.09%)
model generation 19.04 sec ( 38.83%)
optimizer 30.00 sec ( 61.17%)
Post-processing 0.00 sec ( 0.00%)
[19]:
binning_table = optb.binning_table
binning_table.build()
binning_table.analysis()
---------------------------------------------
OptimalBinning: Binary Binning Table Analysis
---------------------------------------------
General metrics
Gini index 0.08891470
IV (Jeffrey) 0.03737164
JS (Jensen-Shannon) 0.00461702
Hellinger 0.00464395
Triangular 0.01825927
KS 0.06087208
HHI 0.19466583
HHI (normalized) 0.13271705
Cramer's V 0.04978528
Quality score 0.00058822
Monotonic trend peak
Significance tests
Bin A Bin B t-statistic p-value P[A > B] P[B > A]
0 1 1.221574 2.690519e-01 1.202075e-01 8.797925e-01
1 2 3.537222 6.000588e-02 3.120268e-02 9.687973e-01
2 3 0.078781 7.789566e-01 3.875777e-01 6.124223e-01
3 4 0.190265 6.626959e-01 3.352569e-01 6.647431e-01
4 5 26.771144 2.290319e-07 1.971027e-08 1.000000e+00
5 6 7.184990 7.351597e-03 9.965864e-01 3.413632e-03
6 7 40.761911 1.719521e-10 1.000000e+00 2.474909e-12
7 8 0.011697 9.138763e-01 5.399700e-01 4.600300e-01
8 9 54.211508 1.800294e-13 1.000000e+00 1.110223e-16
9 10 29.296187 6.211781e-08 1.000000e+00 4.795264e-11
10 11 10.992632 9.147483e-04 9.997649e-01 2.351244e-04
The current solution is IV = 0.03737164, compared to the LocalSolver solver solution 0.03776231. Let us increase the time limit to 200 seconds.
[20]:
optb = OptimalBinning(name=variable, dtype="numerical", solver="cp", max_n_prebins=100,
min_prebin_size=0.001, time_limit=200)
[21]:
optb.fit(x, y)
[21]:
OptimalBinning(cat_cutoff=None, class_weight=None, divergence='iv',
dtype='numerical', gamma=0, max_bin_n_event=None,
max_bin_n_nonevent=None, max_bin_size=None, max_n_bins=None,
max_n_prebins=100, max_pvalue=None,
max_pvalue_policy='consecutive', min_bin_n_event=None,
min_bin_n_nonevent=None, min_bin_size=None,
min_event_rate_diff=0, min_n_bins=None, min_prebin_size=0.001,
mip_solver='bop', monotonic_trend='auto',
name='REGION_POPULATION_RELATIVE', outlier_detector=None,
outlier_params=None, prebinning_method='cart', solver='cp',
special_codes=None, split_digits=None, time_limit=200,
user_splits=None, user_splits_fixed=None, ...)
The optimal solution is found within the time limit.
[22]:
optb.status
[22]:
'OPTIMAL'
[23]:
optb.information(print_level=1)
optbinning (Version 0.18.0)
Copyright (c) 2019-2023 Guillermo Navas-Palencia, Apache License 2.0
Name : REGION_POPULATION_RELATIVE
Status : OPTIMAL
Pre-binning statistics
Number of pre-bins 77
Number of refinements 0
Solver statistics
Type cp
Number of booleans 3155
Number of branches 165953
Number of conflicts 75652
Objective value 37758
Best objective bound 37758
Timing
Total time 148.19 sec
Pre-processing 0.00 sec ( 0.00%)
Pre-binning 0.44 sec ( 0.30%)
Solver 147.75 sec ( 99.70%)
model generation 17.90 sec ( 12.12%)
optimizer 129.84 sec ( 87.88%)
Post-processing 0.00 sec ( 0.00%)
[24]:
binning_table = optb.binning_table
binning_table.build()
binning_table.analysis()
---------------------------------------------
OptimalBinning: Binary Binning Table Analysis
---------------------------------------------
General metrics
Gini index 0.08180326
IV (Jeffrey) 0.03776231
JS (Jensen-Shannon) 0.00465074
Hellinger 0.00468508
Triangular 0.01833822
KS 0.06087208
HHI 0.23425608
HHI (normalized) 0.16464300
Cramer's V 0.05102627
Quality score 0.06257516
Monotonic trend peak
Significance tests
Bin A Bin B t-statistic p-value P[A > B] P[B > A]
0 1 1.445262 2.292897e-01 1.013041e-01 8.986959e-01
1 2 158.939080 1.929529e-36 1.179082e-218 1.000000e+00
2 3 131.200666 2.238000e-30 1.000000e+00 1.110223e-16
3 4 0.878638 3.485750e-01 8.240457e-01 1.759543e-01
4 5 14.925402 1.118468e-04 9.999989e-01 1.123668e-06
5 6 3.969732 4.632513e-02 9.768847e-01 2.311530e-02
6 7 40.662233 1.809509e-10 1.000000e+00 3.330669e-16
7 8 29.296187 6.211781e-08 1.000000e+00 4.795253e-11
8 9 10.992632 9.147483e-04 9.997649e-01 2.351244e-04
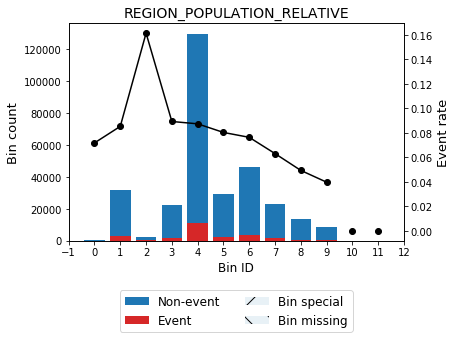
The optimal solution is IV = 0.03776231, matching the LocalSolver solver solution 0.03776231.
[25]:
binning_table.plot(metric="event_rate")